Introduction:
From watching a video to reading this article, everything is possible because of the internet. The Internet has become an inevitable part of our lives.
It has made our life more social. It is because of the internet we are able to communicate with each other, no matter where we are. Also the arrival of social media was another big thing.
Social media like instagram, facebook, twitter etc.. became fundamental for entertainment. Also it is because of the internet we are able to know a lot of things. The Internet helped people gain knowledge and made them aware of things happening all over the world.
During the COVID lockdown, a life without internet would have been terrible. From entertainment to work, the internet had been the main reason for time going during lockdowns.
But do you ever know how the cables in the depths of the ocean help us access the internet and how starlink will revolutionise it?
How do we access the internet?
If you click to watch a video, it has to travel thousands of kilometres before it can reach your computer or mobile phone. It is because your browser sends a request to the google server which is located elsewhere in the globe.
So this request from your device will have to reach the server where that video is stored. Once that request is verified and accepted, the video travels back to the same place where it received the requests. But do you know how these commands/requests travel between your home and the server? Have you ever wondered in what form these signals travel?
There are 2 ways this information travels. The most prominent one is optical fibres.
Underwater cables:
99% of all internet that we access today is from these underwater cables. It's because of these cables we are able to watch UK based mrwhosetheboss channel’s videos even from india. We are able to send messages, GIFS, emoji in whatsapp even to a person who is on the other side of the globe.
Underwater cables are not anything new. The first underwater cable was laid in 1866 between France to Ireland by SS Eastern ship. It was the first time ever an underwater cable was laid successfully. This cable was used to transmit telegraphs which later carried telephone signals as well.
Since then more than 300 cables were laid on the ocean bed which is the backbone for all economic activities including stock market and cryptocurrencies. More developed the country, the more cables it has. For example transatlantic cables connecting Europe and America are more in numbers than the ones that connect africa.
 |
| All underwater cables |
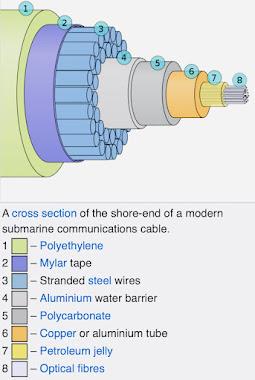
Cyrus West field was the person who proposed the idea to send telegraph via underwater cables in 1854 which was then completed in 1866. This cable consisted of 7 copper wires which could transmit information and was coated with some kind of rubber which acted as an insulation from sea water. Finally layers of iron wirings were on the top to protect it from other physical factors.
But over the years the cables got drastically improved. The below picture depicts the different layers of a typical underwater cable.
Although you can find a lot of changes in the insulation and protective coverings, the most critical change is the transition from copper wires to optical fibres. Unlike sending signals in the form of electrical impulses via the copper wires, the optical fibre uses light to transmit information/data.
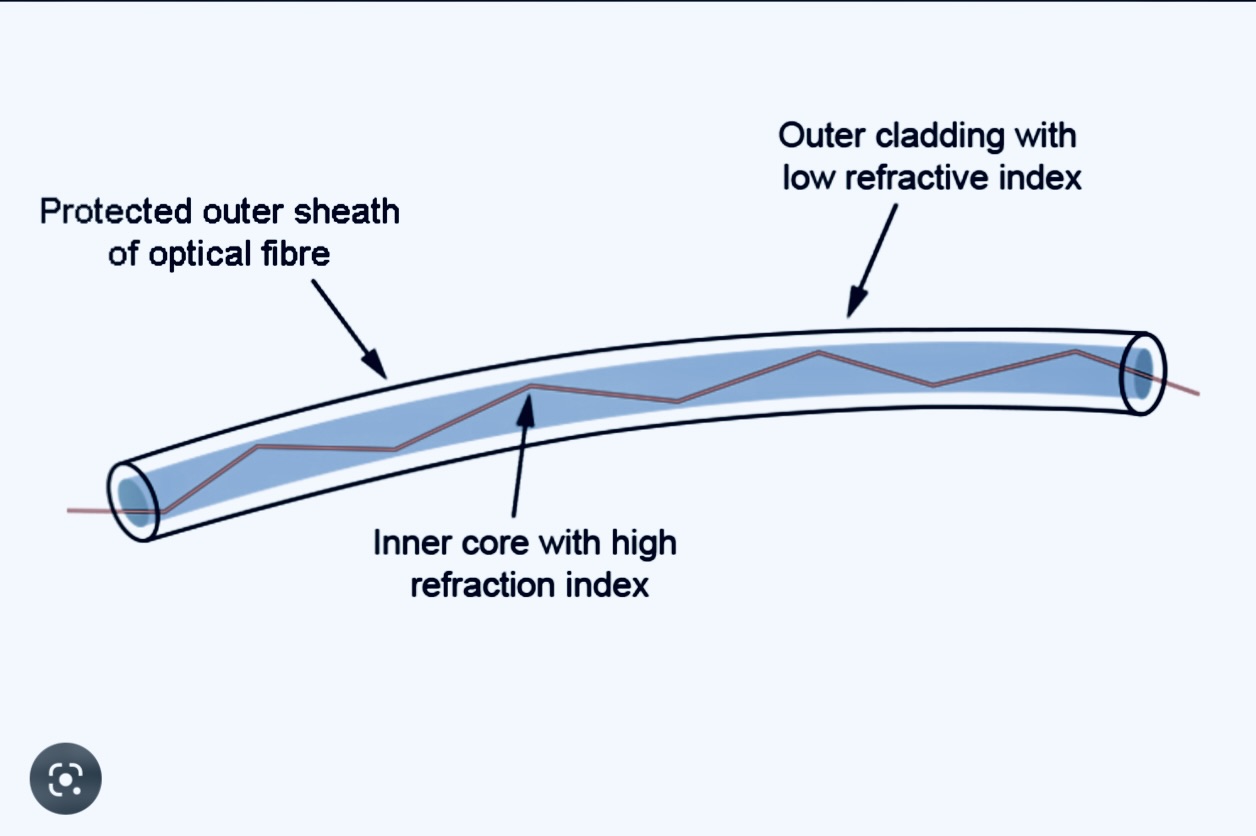 |
| Total internal reflection |
Fibre optics(core of the cable) are made of glass or plastic which could reflect light within itself. The light signals are transmitted via a process named Total Internal Reflection. In this process the light is reflected within the core again and again in a particular angle. The picture below depicts how the light is bounced within the core again and again and travels forth.
Advantages of optical fibres over copper wires.
Because optical fibres transmit information in the form of light signals, it is much faster than conventional electrical impulses. They can also travel data to longer distances without much signal loss.
They are also less interfered by other factors like electromagnetic interference and other sources of noise which usually cause lag in conventional electrical impulses.
Problems with ocean cables:
There are a few problems to tackle with ocean cables. As it is critical to all global communications, it has to be taken care meticulously. So the major problems are:
Natural calamities:
Tsunamis, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions etc cause damage the underwater cables. But earthquake-prone areas like the joints of the tectonic plates and volcanic-prone areas like the Ring of Fire are often avoided. But still problems caused by natural calamities have been identified.
Maintenance challenges:
In case of wreckage, repairing requires whopping high amounts. Extensive and specialised ships are required. This usually results in the delay of repair and causes disruption.
Human factors:
Human factors like fishing, drilling, anchoring etc.. severely damages cables. Accidental anchoring on cables leads to entanglement and wreckage.
Security during danger times:
As being critical to our global network, these might become the targets during the war time. Or other malicious activities by terrorists and other unwanted groups might damage it.
Cannot give internet access to all people:
It is found that more than a third of the world’s population have not used the internet. Because these cables could not help each and every person to access the internet. And not all who receive the internet get the fastest speed. Most of the people living in remote places on the earth had never used the internet and are isolated from the real world.
What is space internet?
This is the second way we can transfer information. Instead of laying cables, we can send satellites to space which can transmit data. The server sends the signal to the satellite and it will redirect it to the designated location. This sounds simple but there are a lot of problems with satellite based internet.
Before getting into its cons, it is first important to understand what latency and bandwidth is.
Latency:
Just imagine a water pipe; the longer the pipe, the more the time it takes for the water to reach the other end. This is what we exactly call latency. The more distance, the more time it takes. This is a major problem with the space internet. As satellites are usually placed 30,000 to 40,000 km high from the ground. It has to travel double the distance. I.e one time to reach the satellite and again it has to travel back to the earth.
As the distance is more, the latency is also high, which is not really good.
Bandwidth:
Just get back to the same pipe analogy. The wider the pipe, more water can pass through it. But, width depends upon the latency(length) of the pipe. A pipe with a length of 1 metre and width of 10 centimetres is considered good. But a pipe with 1 km length and 10cm width is no good.
Although both the pipes are of same width, both are not equally good. Instead of the width of the pipe, replace it with the strength of the signals.
So for a high speed internet it is important to have a low latency and high bandwidth. But a space internet will possess high latency and low bandwidth because of its height.
Now you might raise a question. Although cables connecting countries are not as long as the distance of the satellite from earth, signals still lose their strength travelling thousands of km. Then how do ocean cables tackle it?
This was where some intelligent people came up with “repeaters” which is a type of mission that amplifies light. At every particular distance repeaters were connected to the cables which amplify the light signals. This allows light signals to travel longer distances via ocean cables. But this cannot be possible in space.
Problems with space internet?
Cost:
The first and major problem with space internet is the cost to launch a satellite. Sending something to space is still extremely difficult and expensive. If something goes wrong with the satellite, there is little to no possibility for repair works.
Weather dependent:
As these satellites are located over our atmosphere, they are vulnerable to all sorts of weather related problems. Sending signals will become extremely difficult during bad weather conditions.
Starlink and its competitors:
Although having a lot of hurdles to come across, SpaceX decided to take a leap. But they remain to have the upper hand in the cost of launching satellites. Because of their falcon 9 partially reusable rocket, SpaceX was able to reduce the cost significantly.
But it is not just SpaceX, other companies like UK based OneWeb, Amazon, HughesNet and Viasat have also launched satellites to compete with starlink.
Satellite constellation:
Traditional telecommunication satellites were limited to their number. Only 1 or 2 satellites will be launched which may not be able to cover all parts of the globe at the same time. But these companies which have come forward to make internet satellites a thing have a better idea.
They decided to put a cluster of satellites around orbit which should make coverage easier. This is called satellite constellation.
How is starlink different?
Instead of launching a few hundred big satellites into space, SpaceX decided to launch thousands of small sized satellites. Their goal is to launch 42000 satellites with latency as low as cable internet. They even claimed to provide faster internet than optical fibres if more satellites are launched.
As of now 3328 have been launched. But other companies opted with the traditional method. Recently OneWeb launched 36 satellites from ISRO’S GSLV-MARK-3 rocket. These satellites are huge and more expensive than the one that Starlink creates.
Instead of launching satellites high above over 22000 km (traditional satellite orbit altitude) from earth, starlink satellites are placed in low earth orbit which is just 300 miles or 550 km from ground.
Starlink is a part of SpaceX so frequent launches can be done. This is not the case with other companies. They have to look for other space agencies who could send their satellites to space. Also Falcon 9 made the job easier for SpaceX.
How does starlink work?
Starlink Satellites placed 550 km above us revolve around earth in a stationary orbit called low earth orbit. Generally telecommunication satellites were placed at geostationary orbit which is 36,000 km above us. Due to this vast difference in the location of orbit, latency was drastically lowered in starlink internet.
Also a satellite can transmit data to other satellites using lasers. Starlink calls this technology as Optical Intersatellite links. For example, if a satellite above google’s server(In USA) receives a signal to transmit a video to a person living in Australia.
That satellite may not be able to transmit that data to Australia, because it is over the US and it will be extremely hard for a satellite to connect US and Australia at the same time. So this satellite will transmit this data to a nearby satellite which then passes signals to the next via lasers until it reaches the satellite that is above Australia. This is how Optical Intersatellite links work.
Starlink will also provide you with a starlink dish which is capable of self orientation towards the nearby satellite. The instalment process of starlink dish is simple, but it is required to be placed where the above sky should be clear of obstacles. A terrace or roof is a better option, as it may not be obstructed by trees or other buildings.
This is it. Once you install starlink in your home and follow the other few instructions from the starlink app, you are ready to use the satellite internet yayyy. The dish will self orient itself towards the above available satellite and you need not worry about the dish again.
Pros of starlink:
Space debris has become a real big issue for us. The number of satellites SpaceX claimed to launch is more than the number of satellites humans have ever launched since Sputnik-1(first satellite ever launched). As a result it may lead to a lot of collisions between satellites.
But these starlink satellites are innate with autonomous collision avoidance systems. This prevents these satellites from colliding with other satellites or space debris. A self-destruct feature is also available in starlink satellites which end up falling into the ocean after their lifetime. Thus it helps in avoiding the accelerating space debris problem.
Nearly one third of the world’s population had never seen the internet. No matter where you are, how remote the place is, Starlink will be able to deliver us high speed internet.
Fun fact:
You can also access the internet anywhere in the ocean with starlink. They claim to provide 220 Mbps of download speed anywhere in the ocean. So the next time, when going for a treasure hunt never forget to get a starlink kit with you. In case of emergency you can contact the pirates for help (who probably should have a starlink kit too).
Problems with starlink:
So far there are 5000 satellites above us along with a lot of space debris. Now just imagine 1 company launching 8 times the number of satellites humanity has ever launched in its lifetime. It's ridiculous. This has infuriated a lot of space observers.
Having 40000 satellites a few kilometres above them will completely disrupt their space observatory telescopes. They will never be able to keep track of objects in space. Simply space observation from earth will become impossible. You can even see satellites flying above you with naked eyes if freaking 40000 satellites were launched.
 |
| All Starlink Satellites soo far launched |
Both the quantity and its altitude is a big problem for space explorers.
The other major hurdle for starlink is the weather. During the times of heavy rain and snowfall, internet connection from these satellites will not be available. Also during the times of extreme fog or dark heavy clouds will disrupt your signals. Wind will never be a problem, unless it is a hurricane or a cyclone.
Will this really matter to us?
Although Elon Musk claims that it will help people living in remote places, it is to be understood that he is a businessman. The estimated revenue that starlink will bring to SpaceX in the near future, will be much higher than the fundings provided by the US government to NASA.
But there is still a long way to go. The current cheapest package from starlink is $110 per month. We can get the internet much cheaper from underwater cables. But this will be a dealbreaker for people who had never seen the internet before in their life. Currently Starlink is available only in few specific countries. the picture below should give you more specific details about it.









0 Comments